Building your own scraping stack can feel thrifty at first: spin up a few cloud instances, bolt on headless browsers, and call it a day. Six months later you’re juggling IP bans at 3 a.m., burning compute on retries, and filing extra compliance paperwork. Below, we unpack those often-ignored costs and show where controlled proxy rotation quietly delivers the biggest savings.

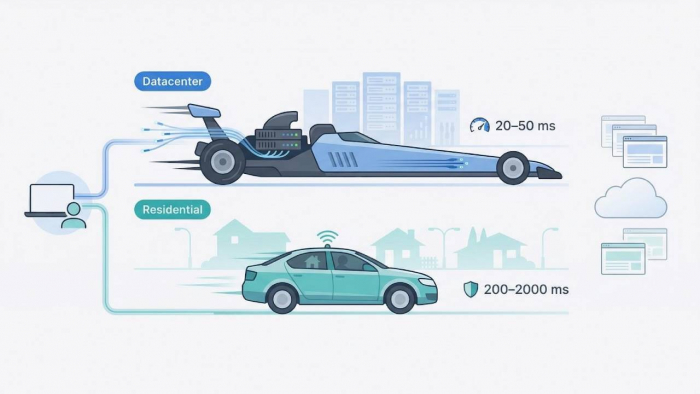
The Real-World Load Behind Every HTTP Request
Automation is no longer a niche edge case it dominates the wire. Imperva’s 2024 Bad Bot Report pegs non-human traffic at almost half of everything on the public internet, with “bad bots” alone responsible for 32 % of total volume.
That means every request your crawler fires must elbow through the same congested lanes as sneaker bots, carding scripts, and credential stuffers. Latency spikes aside, this hostile background noise forces in-house teams to over-provision bandwidth and keep escalation runbooks handy expenses few spreadsheets predict.
Operational Costs Nobody Budgets For
People hours eclipse cloud bills faster than most engineers admit. Forrester’s September 2024 Total Economic Impact study of a global retailer found that consolidating edge security and bot-mitigation tooling cut unplanned downtime by the equivalent of $957 000 over three years and produced a 238 % ROI, thanks largely to a 29 % lift in security analyst productivity.
Flip the numbers: had the retailer stayed with its patchwork, those seven-figure losses would persist as a silent tax. DIY scraping setups suffer a similar fate each ban cycle means developers rewrite retry logic, rotate headers, or rebuild session stores instead of shipping features.
Compliance and Risk: The Invisible Multiplier
Scraping isn’t only a technical arena; it’s a regulatory minefield. IDC’s December 2022 Security Operations Center survey notes that while 82 % of U.S. enterprises have vulnerability-scanning tools, just 34 % scan weekly and only 26 % audit more than 85 % of known assets.
Those gaps leave plenty of room for outdated libraries that leak personally identifiable information or violate a platform’s terms of service. Legal teams generally price risk higher than engineers do. Multiply potential fines, takedown demands, and brand-damage remediation, and the “cheap” scraper starts looking like a liability.
Why Smarter Proxy Rotation Alters the Equation
Akamai’s 2024 web-scraping impact study measured 42.1 % of observed traffic as bot-generated, with 65.3 % classified as outright malicious.
Rotating residential or ISP-level IPs evens the playing field: you mimic organic diversity, dodge reputation scoring, and distribute load so each target sees a trickle instead of a flood. Done right, rotation slashes ban-related redeploys, stabilizes success-rate metrics, and chills the pager.
Managed services bake in fresh IP supply, geographic choice, and automated ethical-use controls. Teams that once hand-rolled scripts to cycle proxies can now simply buy rotating proxy capacity, focus on parsing data, and let the provider absorb churn, legal vetting, and carrier-level negotiations.
A Quiet, Compounding Advantage
Infrastructure costs rarely explode in a single headline incident; they bleed budgets through overtime, bandwidth spikes, and compliance fire drills. Validated data shows the bulk of web traffic and a growing share of security spend now revolves around mitigating or masquerading as automated activity. Hand-built scraping rigs struggle to keep pace.
Swapping brittle IP pools for orchestrated rotation doesn’t just unblock requests; it buys back developer hours, lowers legal exposure, and stabilizes success rates. In short, the cheapest scraper is the one you never notice because it simply works.
Post Comment
Be the first to post comment!